Biochemical Sensors for Wound Monitoring
ASSIST is developing novel smart dressings (gauzes) for monitoring wound healing. These smart dressings monitor the patients’ wound severity, correlating progression through its healing stages, to help determine proper treatment and therapeutic efficacy while continuing to provide a current standard of care. This approach can facilitate improved diabetic wound management by enabling timely therapeutic interventions.
Real-time wound monitoring technology does not exist. This ASSIST research is creating new technology. The research is using novel nanomaterials and architectures to create stable sensors that work at the body and ambient high temperatures.
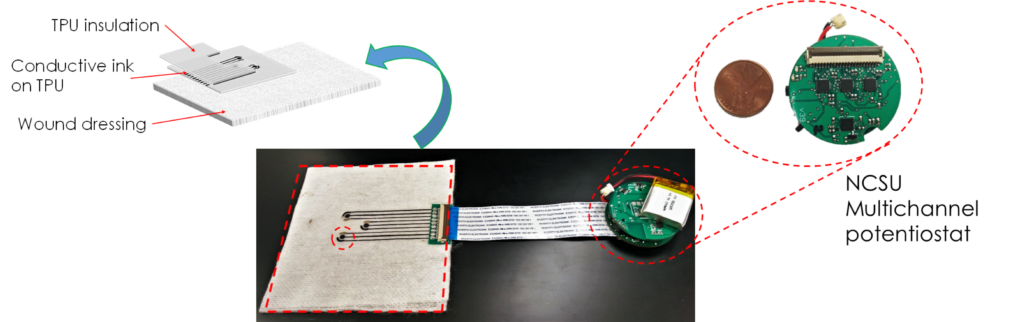
The technology focuses on translating enzymatic electrochemical techniques to gauzes for point-of-care measurements. The fundamental sensing challenge is that enzymatic activity fades with time and temperature. ASSIST’s approach is to use novel nanomaterials to stabilize the enzymatic sensor activity while maintaining its selectivity and thermal stability. ASSIST’s approach leverages multimodal sensors co-fabricated on dressings and gauzes for correlation of health parameters to determine the efficacy of wound healing and diagnostics. The technology can be seamlessly integrated into ASSIST’s low-powered wearable system-on-chip for long term wound monitoring. One of the biggest applications of this technology is the monitoring of diabetic wounds.
